
TOP-10 US Cities with the Lowest Rents
When analyzing more than 1,100 U.S. counties, a clear geographic pattern emerges: The highest rents are concentrated along the West and East Coasts, while the most affordable housing is found in the Midwest. Among the 342 to 351 U.S. cities with populations over 100,000, there is a dramatic gap in rent costs, ranging from $625 per month in small, rural towns to more than $3,500 in major metropolitan areas. This study will help you understand where in the U.S. you can find the most affordable rental housing and what factors influence these differences.
The data on average rents for housing in the United States was taken from housing data from the Zillow portal, the largest residential real estate platform in the United States. Before talking about the cities with the cheapest rents for housing, let’s go up a few levels in the hierarchy of US territorial divisions.
Current Overview of the US Rental Market
In June 2025, the typical rent in the United States was $2,069, up 2.9% from June last year. According to Zillow, the Observed Rent Index in the United States has been growing over the past ten years. However, the largest increase was noted during the coronavirus pandemic, or more precisely, between January-March 2021 and September-October 2022. If at the beginning of this period, the typical rent in the United States was $1,527, then by the end of the period, it reached $1,950 — during this period, the typical rent increased by 27.7%.
Regional Geography of Rental Rates
Now, in the administrative-territorial hierarchy of the United States, we will go down to the counties, intentionally skipping the main territorial unit — the state, since typical rent can vary significantly from county to county within the state itself.
According to the classification of the United States Census Bureau, there are 3,006 counties and 138 of their equivalents (independent cities, parishes, one federal district, and other special units) in the country — a total of 3,144 county-type units in the country.
Housing data from the Zillow portal contains information on the average rent for housing in 1,163 counties. For clarity, REALTING below provides a map of the average rent by US county in June 2025. It is worth noting that not all districts have any active rental market, and according to some estimates, about 60% of districts can be characterized as rural, where it is not possible to collect statistics on average rental rates.
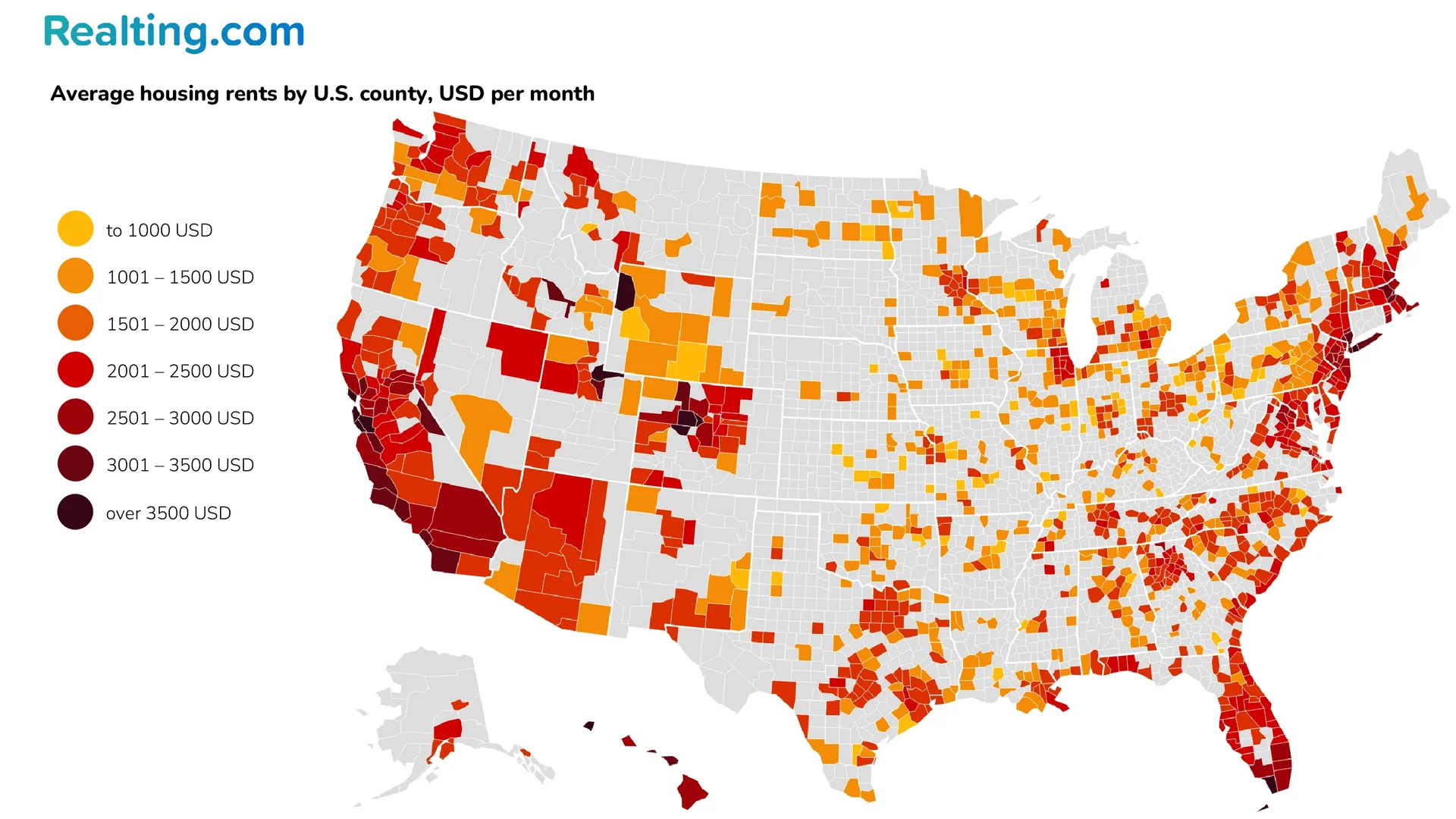
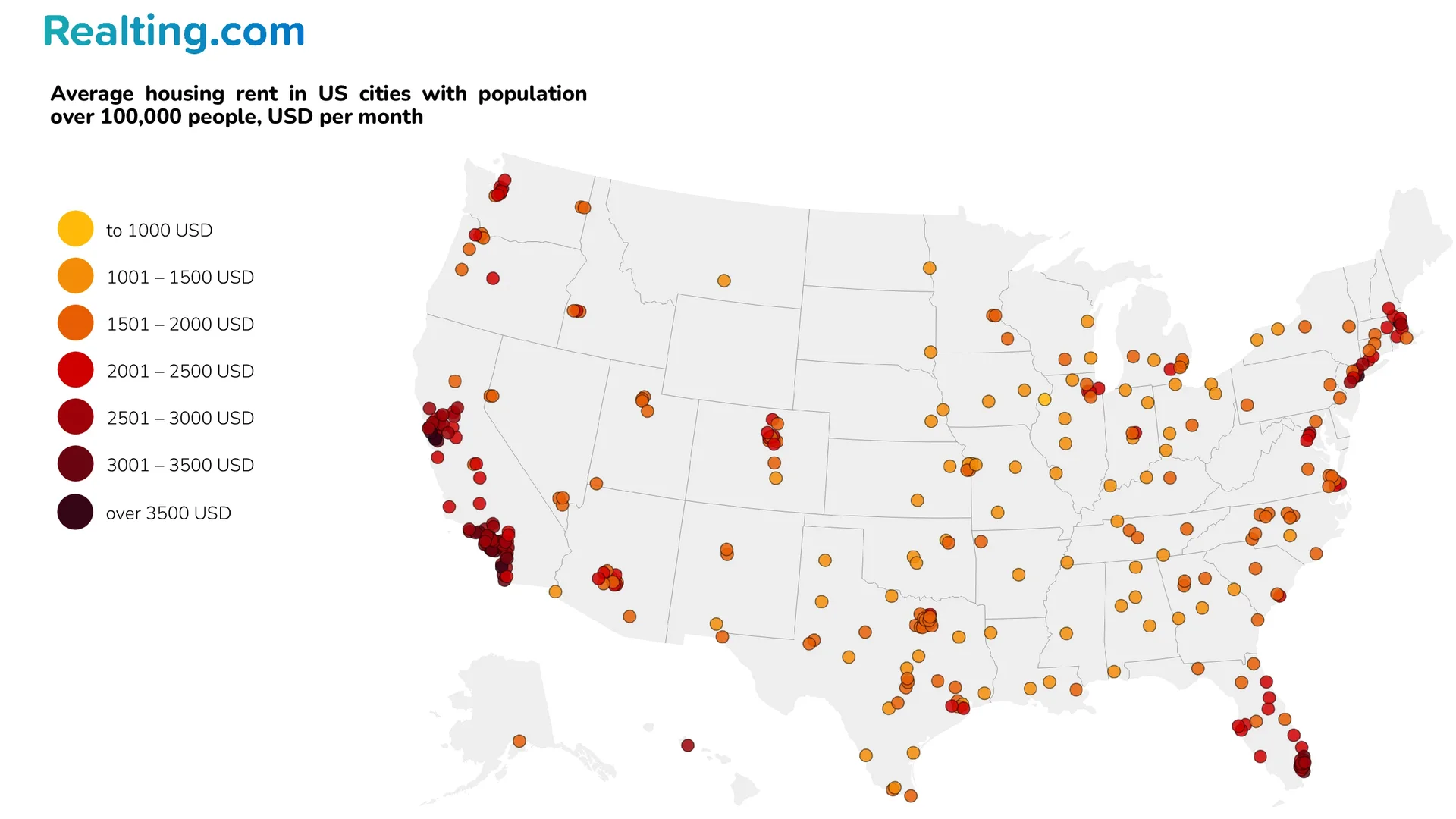
The map clearly shows how typical housing rent varies by US counties depending on regional location. Housing rent is most expensive in counties that are located along the West and East coasts of the US, followed by counties in the southern part of the US. In turn, the cheapest counties for rent are in the Midwest of the US. From the counties of the United States, we finally move on to cities. In this case, we will consider only cities with a population of at least 100,000 people — according to various sources, there are from 342 to 351 such cities in the US.
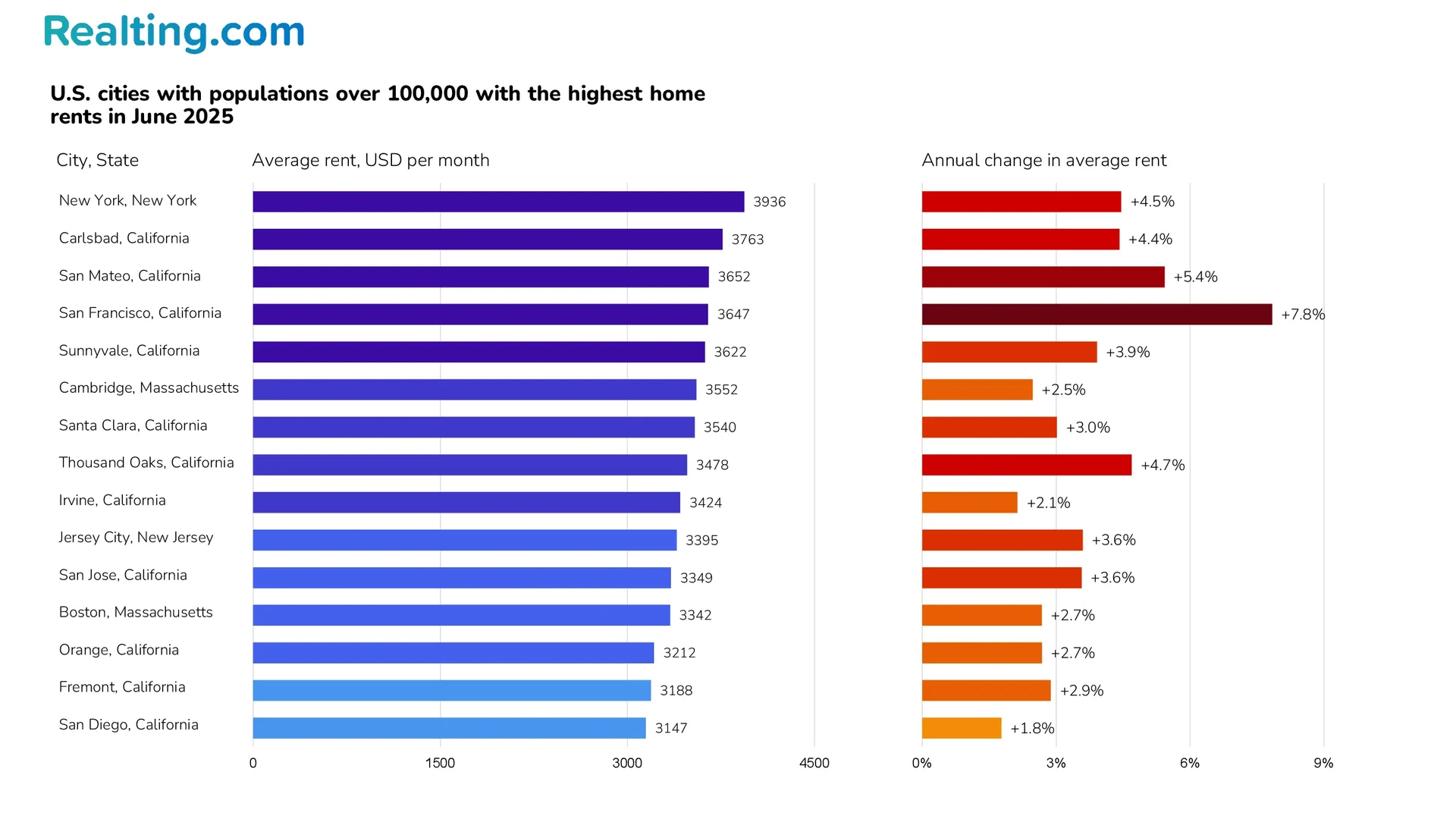
The Most Expensive Cities in the U.S. to Rent
According to housing data from Zillow, in June 2025, the typical market rent in the United States exceeds $3,500 per month in 7 cities — in 19 cities, the typical rent ranges from $3,001 to $3,500 per month. The cities with the most expensive residential rent are most often found in these states: California, Florida, New Jersey, New York, Massachusetts.
US Cities With the Most Affordable Rents
As of June 2025, there are 71 cities in the United States with populations greater than 100,000 where the typical rent is less than $1,500 per month.
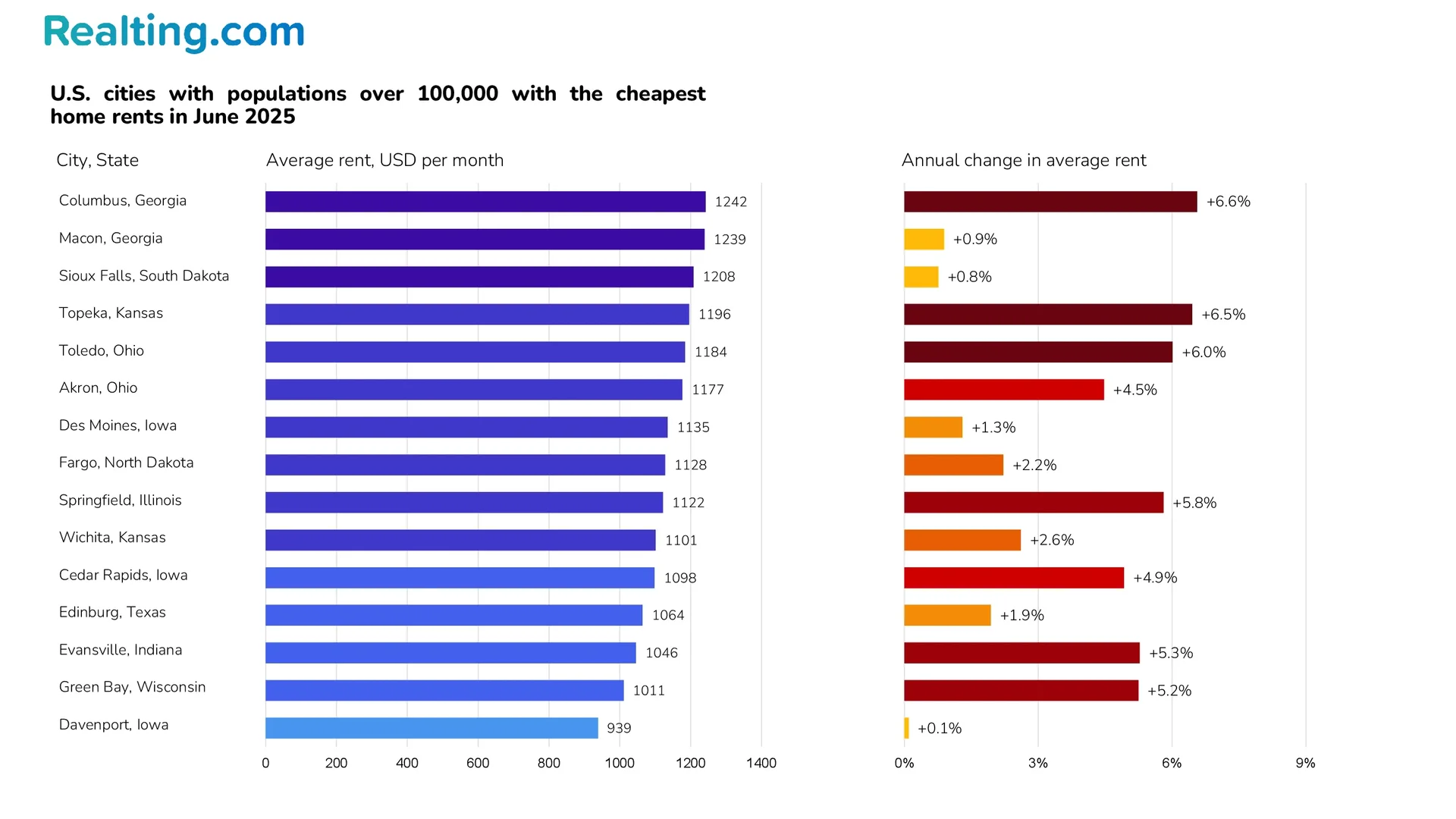
However, there are cities in the US where the average monthly rent does not exceed 800 USD. Most often, such cities are found in the Midwestern states: the population of such cities rarely exceeds 30,000 residents, these cities are not part of agglomerations, they do not have large enterprises, and, in general, they can be described as “American hinterland.”
Top 10 US Cities with the Cheapest Rents in June 2025:
|
City, State |
Typical rent, USD per month (according to Zillow) |
|
South Tucson, Arizona |
625 |
|
Carbondale, Illinois |
683 |
|
Valley City, North Dakota |
697 |
|
Emporia, Kansas |
711 |
|
Rolla, Missouri |
725 |
|
East Grand Forks, Minnesota |
743 |
|
Dyersburg, Tennessee |
758 |
|
Boone, Iowa |
759 |
|
Athens, Ohio |
774 |
|
Hutchinson, Kansas |
781 |
What’s the Bottom Line?
Based on an analysis of Zillow data, it’s clear that geography has a significant impact on rental housing affordability in the U.S. The best deals for renters are concentrated in smaller Midwestern cities, where typical rents can be under $800 per month. These communities, like South Tucson, Arizona ($625) and Carbondale, Illinois ($683), offer alternatives to expensive coastal metropolises, albeit with some tradeoffs in career opportunities and urban amenities.
The three-fold difference between the cheapest and most expensive rental markets reflects deeper economic and demographic trends in American society. For those willing to consider moving to smaller cities or working remotely, the Midwest and select Southern cities offer significant opportunities to save on housing. It’s important to consider, however, that lower rents often correlate with fewer job opportunities and fewer city services, making where you live a matter of individual priorities and life circumstances.




















