
US Taxes. Top States with the Lowest and Highest Taxes
The tax system forms the foundation of any state, and the United States is no exception. However, due to the high degree of autonomy granted to individual states, there is no unified federal tax rate in the U.S. Instead, each state determines its tax rates and overall tax burden based on local circumstances.
This creates a situation where the total tax burden varies significantly between states. For example, California and New York impose income taxes of 13–13.5%, whereas states like Florida, Alaska, and Texas have no income tax at all.
In this article, we will take a detailed look at the main types of taxes in the United States, including income taxes, property taxes, sales taxes, excise taxes, as well as taxes affecting businesses and retirees.
Key Takeaways
A person living in one state can also pay taxes to the governments of other states and localities where they do not reside.
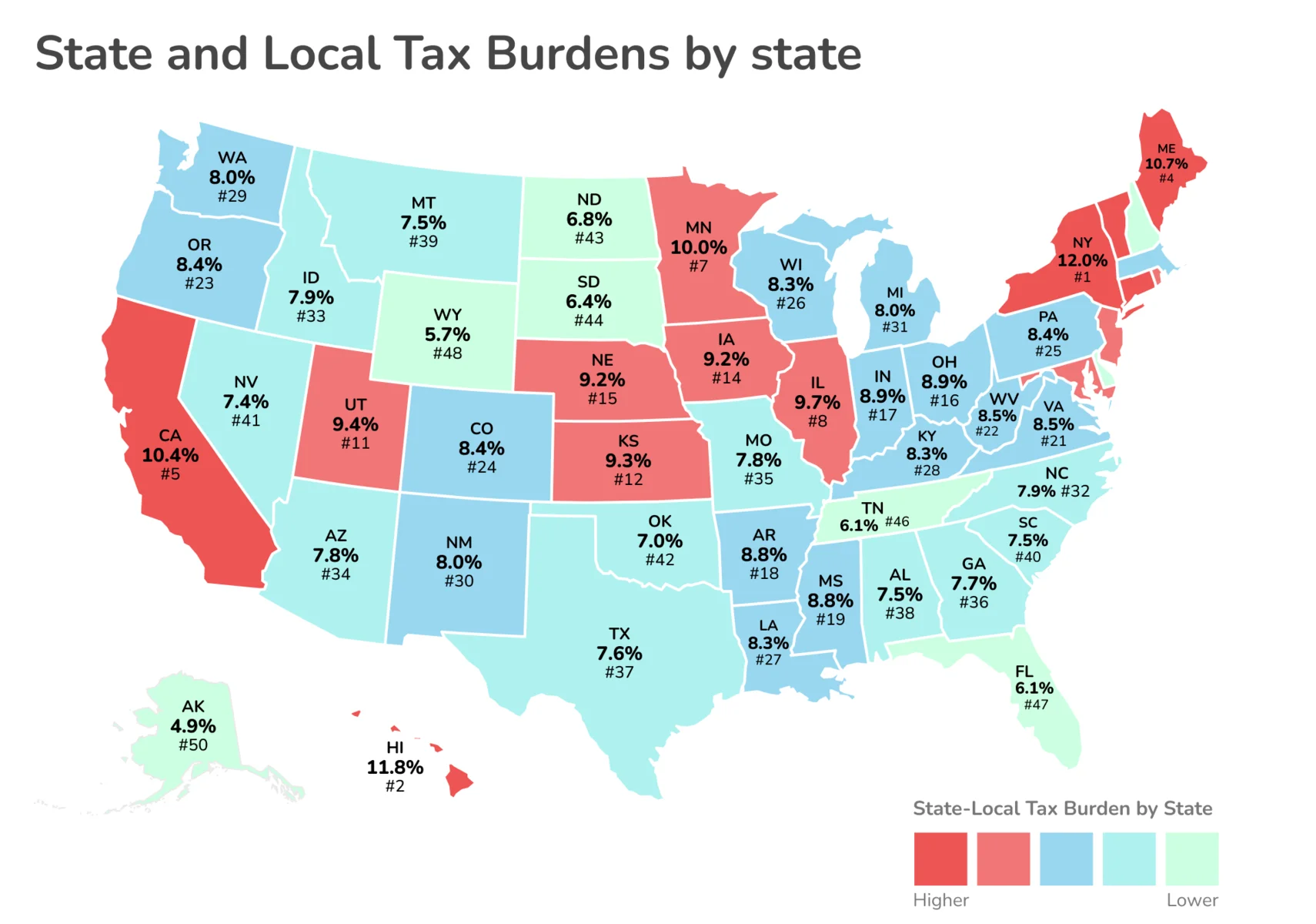
In 2024, New York had the highest total tax burden at 12.0%.
For income tax rates in America in 2024:
- States with the lowest income tax included:
- Colorado: 4.40%.
- Illinois: 4.95%.
- Indiana: 3.15%.
- Pennsylvania: 3.07%.
- Michigan: 4.05%.
- North Carolina: 4.75%.
- Highest income taxes by state:
- California: 13.30%.
- Hawaii: 11.00%.
- New Jersey: 10.75%.
- Oregon: 9.90%.
- Minnesota: 9.85%.
- New York: 10.90%.
The U.S. States with no taxes (personal income taxes) in 2024 are Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming.
Alaska has the lowest income tax in the United States. The state imposes neither a personal income tax nor a state sales tax. Instead, Alaska relies heavily on revenues from the oil and gas industry to fund public services and government operations.
Property tax is calculated as the product of the tax rate and the assessed value of the property. Property can include real estate and/or tangible personal items.
Taxes and Total Tax Burden in the USA
In the United States, the tax system includes federal, state, and local taxes, which together constitute the overall tax burden for residents. The overall tax burden represents the share of residents’ aggregate income that is allocated to federal, state, and local taxes.
The state and local tax burden is a measure that reflects the total amount of taxes collected by state and local governments, calculated on a per capita basis and divided by the share of the gross national product attributed to the state. This measure accounts not only for taxes paid by residents within their state but also for taxes paid in other jurisdictions.
An infographic and table with updated tax rates and the most recent data on the tax burden by the state is provided below:
|
State |
Total tax burden (%) |
Tax burden ranking |
|
New York |
12.0% |
1 |
|
Hawaii |
11.8% |
2 |
|
Vermont |
11.1% |
3 |
|
Maine |
10.7% |
4 |
|
California |
10.4% |
5 |
|
Connecticut |
10.1% |
6 |
|
Minnesota |
10.0% |
7 |
|
Illinois |
9.7% |
8 |
|
New Jersey |
9.5% |
9 |
|
Rhode Island |
9.4% |
10 |
|
Utah |
9.4% |
11 |
|
Kansas |
9.3% |
12 |
|
Maryland |
9.3% |
13 |
|
Iowa |
9.2% |
14 |
|
Nebraska |
9.2% |
15 |
|
Ohio |
8.9% |
16 |
|
Indiana |
8.9% |
17 |
|
Arkansas |
8.8% |
18 |
|
Mississippi |
8.8% |
19 |
|
Massachusetts |
8.6% |
20 |
|
Virginia |
8.5% |
21 |
|
West Virginia |
8.5% |
22 |
|
Oregon |
8.4% |
23 |
|
Colorado |
8.4% |
24 |
|
Pennsylvania |
8.4% |
25 |
|
Wisconsin |
8.3% |
26 |
|
Louisiana |
8.3% |
27 |
|
Kentucky |
8.3% |
28 |
|
Washington |
8.0% |
29 |
|
New Mexico |
8.0% |
30 |
|
Michigan |
8.0% |
31 |
|
North Carolina |
7.9% |
32 |
|
Idaho |
7.9% |
33 |
|
Arizona |
7.8% |
34 |
|
Missouri |
7.8% |
35 |
|
Georgia |
7.7% |
36 |
|
Texas |
7.6% |
37 |
|
Alabama |
7.5% |
38 |
|
Montana |
7.5% |
39 |
|
South Carolina |
7.5% |
40 |
|
Nevada |
7.4% |
41 |
|
Oklahoma |
7.0% |
42 |
|
North Dakota |
6.8% |
43 |
|
South Dakota |
6.4% |
44 |
|
Delaware |
6.4% |
45 |
|
Tennessee |
6.1% |
46 |
|
Florida |
6.1% |
47 |
|
Wyoming |
5.7% |
48 |
|
New Hampshire |
5.6% |
49 |
|
Alaska |
4.9% |
50 |
Source: Visual Capitalist, Tax Foundation
Income Taxes in the United States
Income tax in the United States of America is a primary source of federal revenue and is levied on individuals, corporations, trusts, and other entities. The tax system is progressive, meaning that tax rates increase with higher taxable income levels.
Federal income tax:
- Taxpayers. U.S. citizens, permanent residents (green card holders), and non-residents with U.S. income sources or residing in the U.S. on temporary visas are required to file federal tax returns and pay taxes on their worldwide income. This also applies to investors and business owners.
- Tax rates. Federal income tax rates range from 10% to 37%, depending on income levels and filing status.
- Deductions and credits. Taxpayers can reduce their taxable income using standard or itemized deductions. They may also benefit from tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the Child Tax Credit.
In addition to federal taxes, most states impose their own income taxes.
Tax rates and structures vary:
- Some states use flat rates.
- Others have progressive systems similar to the federal structure.
- A few states do not impose an income tax at all (e.g., Florida, Texas, Wyoming).
Self-employment tax:
- Tax obligation. Self-employed individuals are required to pay the Self-Employment (SE) Tax, which covers contributions to Social Security and Medicare.
- Estimated payments. They must also make quarterly estimated tax payments.
- Tax forms. Income is reported using Schedule C (Form 1040), and SE tax is calculated using Schedule SE.
The combination of federal and state income taxes, along with specific requirements for self-employed individuals, ensures that the U.S. tax system remains comprehensive and accommodates various income sources.
What States Don’t Have a State Income Tax?
Some U.S. states do not levy personal income taxes. These states compensate for the absence of income tax through other revenue sources, such as higher sales taxes or property taxes. In states rich in natural resources, lower tax collections are often offset by income from those resources (e.g., oil revenues in Alaska and Texas).
States with zero income tax:
- Alaska
- Florida
- Nevada
- South Dakota
- Texas
- Washington
- Wyoming
Both New Hampshire and Tennessee previously taxed only income from interest and dividends. But Tennessee has fully eliminated this tax, and New Hampshire plans to eliminate taxation on interest and dividends by 2027.
States with the Lowest Income Tax
States with the lowest income tax rates are often more attractive for doing business because, unlike states without an income tax, they do not compensate for low rates with other high taxes.
States with the lowest taxes (income tax):
|
State |
Tax rate |
|
Colorado |
4.40% |
|
Illinois |
4.95% |
|
Indiana |
3.15% |
|
Pennsylvania |
3.07% |
|
Michigan |
4.05% |
|
North Carolina |
4.75% |
Many of the states mentioned use a flat tax rate for all taxpayers, regardless of their income. This means that even those with higher earnings pay the same percentage, which is particularly beneficial for large businesses.
States with the Highest Income Tax
In some states, the income tax is progressive and directly depends on the income earned. This means that the tax rate increases to its maximum at higher income levels.
Highest taxing states (income tax):
|
State |
Minimum tax rate |
Maximum tax rate |
|
California |
1.00% |
13.30% |
|
Hawaii |
1.40% |
11.00% |
|
New Jersey |
1.40% |
10.75% |
|
Oregon |
4.75% |
9.90% |
|
Minnesota |
5.35% |
9.85% |
|
New York |
4.00% |
10.90% |
Property Taxes in the United States
Property tax in the United States is levied on property owners at the county level and there are no states with no property tax. The tax rate is usually set as a percentage of the property’s value, which is determined based on an assessment by the tax authorities (assessed value). The assessed value is often lower than the market value, and the tax rate varies depending on the state, typically ranging from 0.3% to 2% or higher. For example, the highest rates are found in states with high population density and significant public service costs, such as New Jersey or Illinois. At the same time, in states with predominantly rural areas, like Hawaii or Alabama, the tax burden is minimal.

States with Low Property Tax
Property taxes are levied in all U.S. states; however, some states set minimal rates, reducing the tax burden on property owners. Regions with the lowest state property tax:
- Hawaii: 0.27%.
- Alabama: 0.42%.
- Louisiana: 0.43%.
- Delaware: 0.55%.
- West Virginia: 0.49%.
- South Carolina: 0.57%.
- Arkansas: 0.62%.
- Mississippi: 0.65%.
- Tennessee: 0.68%.
- Wyoming: 0.61%.
Highest Property Tax States
The highest property taxes in the USA are found in states with the highest population density and significant spending on public services and infrastructure maintenance. The highest property tax states:
- New Jersey: the average property tax rate is around 2.2%.
- Illinois: the average property tax rate is around 2.05%.
- New Hampshire: the average property tax rate is around 1.9%.
Sales and Excise Taxes in the United States
In the United States, sales and excise taxes are levied on goods and services at the time of purchase or consumption. These taxes vary by state and include both retail sales taxes and special excise taxes on specific goods (such as tobacco, alcohol, or fuel).
- Sales tax is charged on the purchase of goods or services. In most states, this tax is mandatory, but the rate can range from 0% to 10% or more, depending on the state.
- Excise taxes are levied on items such as alcohol, tobacco, gasoline, and other consumables. These taxes are typically already included in the price of the product at the time of purchase.
The rates and types of these taxes can vary widely depending on the state’s policies and specific state-local requirements.
Zero Sales Tax States
In the United States, there are several states with no sales tax. However, the absence of a sales tax in the USA states is often compensated by other types of taxes, such as income taxes or property taxes. For example, in Oregon, the property tax rate can reach 9.9%.
Zero sales taxes in the United States:
- Alaska
- Delaware
- Montana
- New Hampshire
- Oregon
It’s important to note that in Alaska, local municipalities can impose their own taxes, typically ranging from 1% to 7%, and in Montana, these taxes can go up to 3%.
States with Highest Sales Tax
In some states, sales taxes are significantly higher due to additional local taxes and surtaxes. For example, in California, the state sales tax rate is 7.25%, but when local taxes are included, the rate in large cities can rise as high as 10.5%, making it one of the highest sales taxes in the United States.
States with the US highest tax rate:
|
State |
Base tax rate |
Maximum tax rate |
|
California |
7.25% |
10.5% |
|
Tennessee |
7% |
9.75% |
|
Alabama |
4% |
11% |
|
Louisiana |
4.45% |
11.45% |
|
Oklahoma |
4.5% |
11% |
States with the Lowest Sales Tax
There are also several states with the lowest sales tax in the United States. In these states, the sales tax can be as low as a few percentage points:
|
State |
Base tax rate |
|
Colorado |
2.9% |
|
Missouri |
4.225% |
|
Oregon |
0% |
|
Alaska |
0% |
|
New Hampshire |
0% |
Business Taxes
Business taxation rate in the USA involves several levels and types of taxes, which depend on the company’s legal structure, location, and type of business activity. The main types of taxes that businesses encounter include:
Federal corporate income tax. The corporate income tax rate is 21% on the company’s taxable income. States also impose their own corporate income tax, with rates varying by state. For example:
- California: 8.84%.
- New York: 7.1%.
- Pennsylvania: 9.99%.
Some states, such as Nevada and South Dakota, do not impose a corporate income tax.
Employment taxes. Employers are required to withhold federal income tax from employees’ wages. The withholding amount is based on the employee’s W-4 form. These taxes include:
- Social security contributions: The total rate is 12.4%, split equally between the employer and the employee (6.2% each).
- Medicare contributions: The total rate is 2.9%, also split equally (1.45% each).
Self-employment tax. Sole proprietors and partners in partnerships must pay self-employment tax, which covers their contributions to Social Security and Medicare. The total self-employment tax rate is 15.3%.
Sales tax. There is no federal value-added tax (VAT) in the U.S. However, states and local governments impose sales taxes on goods and services. Rates and regulations vary by jurisdiction.
Property taxes. There are no states with no real estate tax in the US. Local governments impose property taxes on real estate used for business purposes. The rates and valuation methods depend on the location of the property.

Best States for Business Taxes
Choosing the right state for doing business in the U.S. is crucial, as tax policies, business expenses, and access to the workforce vary significantly from state to state. Here are several states that are considered some of the best states for business taxes:
- Texas. One of the fastest-growing states with a strong economy and diverse industries, from technology to energy. Texas has no personal income tax but imposes a business income tax (Franchise tax), which is lower than in many other states.
- Florida. Florida boasts a strong economy and hosts business incubators for startups, with measures to support small businesses. Like Texas, Florida has no personal income tax, and the corporate tax rate is 4.458%, one of the lowest in the U.S.
- Nevada. Nevada has no personal income tax, small business profits tax, or corporate tax. The state offers programs to support new businesses, including job creation incentives and economic growth initiatives.
- Utah. Personal income tax and corporate tax rates in Utah are 4.95%, which is lower than in many other states. The state actively supports startups by offering tax credits and other incentives.
- Colorado. In Colorado, the personal income tax and corporate tax rates are both 4.55%. The state is known for its developed technology and startup ecosystem, particularly in cities like Denver and Boulder.
- North Carolina. The personal income tax rate in North Carolina is 5.25% and counts as the state with the lowest corporate tax rate (2.5%).
- Arizona. In Arizona, the personal income tax rate is 2.59% (for income up to $54,000), and the corporate income tax rate is 4.9%.
States with No Capital Gain Tax
There are several states in the U.S. that do not impose a capital gains tax, significantly reducing the tax burden for business owners and individual investors. No capital gains tax states:
- Florida
- Texas
- Nevada
- Wyoming
- Alaska
- North Dakota
- Tennessee
Retirement Taxes
Taxation of retirement income in the U.S. depends on the type of account, the age of the recipient, and the nature of the withdrawals. For example, when withdrawing funds from traditional IRAs and 401(k) plans, the amounts are subject to federal income tax at the standard rate applicable in the year the funds are withdrawn. Federal income tax rates range from 10% to 37%, depending on the total taxable income and filing status. Additionally, if funds are withdrawn from a retirement account before reaching the age of 59.5, an additional 10% early withdrawal penalty applies.
Contributions to a Roth IRA are made from already taxed income and are not deducted from taxable income in the year of contribution. Withdrawals after the age of 59.5, provided the account has been open for at least 5 years, are not subject to federal income tax. However, early withdrawals are also subject to a 10% penalty.
There is also the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT), which is 3.8% and applies to net investment income if the adjusted gross income (AGI) exceeds the following thresholds:
- $250,000 for married couples filing jointly.
- $200,000 for single filers.
- $125,000 for married individuals filing separately.

Best States to Retire in for Taxes
For retirees looking for regions with minimal or no taxes in states, several states in the U.S. offer more favorable conditions for residency. Here is the list of retirement friendly tax states:
- Florida. Florida is one of the most popular states for retirees due to its lack of state income tax. This means that pension income and other types of income (such as dividends and interest) are not taxed at the state level.
- Tennessee. Tennessee is one of the states with no retirement income tax, and the tax on interest and dividends was abolished in 2021. However, property taxes in Tennessee are higher than the national average.
- Texas. One of the wealthiest states in the U.S., Texas is a state with no tax on retirement income. Although Texas is not the cheapest property tax state which is above average, the state’s well-developed infrastructure and strong social benefits attract retirees.
- Alaska. Alaska does not levy an income tax, and residents receive an annual dividend through the Alaska Permanent Fund. However, this is the northernmost state in the U.S., and the cold climate may not be ideal for everyone.
- Wyoming. Wyoming is a state with no taxes on retirement, and also offers low property taxes and senior benefits, making it an attractive state for retirees.
- Montana: Montana imposes income tax, but in some cases, retirees can receive tax deductions through special exemptions.
- South Carolina. South Carolina provides tax benefits for retirees, including exemptions on a portion of pension income and Social Security benefits. The state has a moderate property tax, and retirees can qualify for discounts on property taxes.
- Delaware. Delaware does not tax pensions or Social Security benefits, and its property tax rate is one of the lowest in the U.S. So it is probably one of the best states to retire in for taxes.
Author
I write informative articles about real estate, investments, job opportunities, taxes, etc.






















