
Why is it so hot? Droughts that changed the world and continue to change it right now
A UN report says that since 2000, the frequency and duration of droughts have increased by nearly a third. Right now, a historic drought is killing hundreds of dolphins in the Amazon rainforest and forcing people from their homes. What other areas are currently experiencing droughts, and why are they even happening? Why was the summer of 2023 the hottest in history? Which droughts have been the worst in history? We tell you about all this in our article.
What is a drought, and what causes it?
Drought is a natural phenomenon in which, for a long time in a certain region, there is a lack of precipitation and, as a result, a decrease in the level of moisture in the soil and water resources.
The following factors can contribute to the occurrence of droughts:
- Global climate change can lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of droughts.
- Human activities, such as excessive water consumption in agriculture, industry, and households, can exacerbate drought problems, especially in regions with limited water resources.
- Destruction of forested areas and alteration of natural vegetation can affect the hydrologic cycle and contribute to droughts.
- Geographic characteristics. Some regions are more susceptible to droughts because of their geographic location and climatic conditions. For example, deserts and semi-deserts are often prone to long-term droughts.
Droughts can have serious negative impacts on the environment, agriculture, the economy, and society as a whole.
Where are droughts being experienced right now?
Droughts are currently being dealt with in many different parts of the world. Here are some examples.
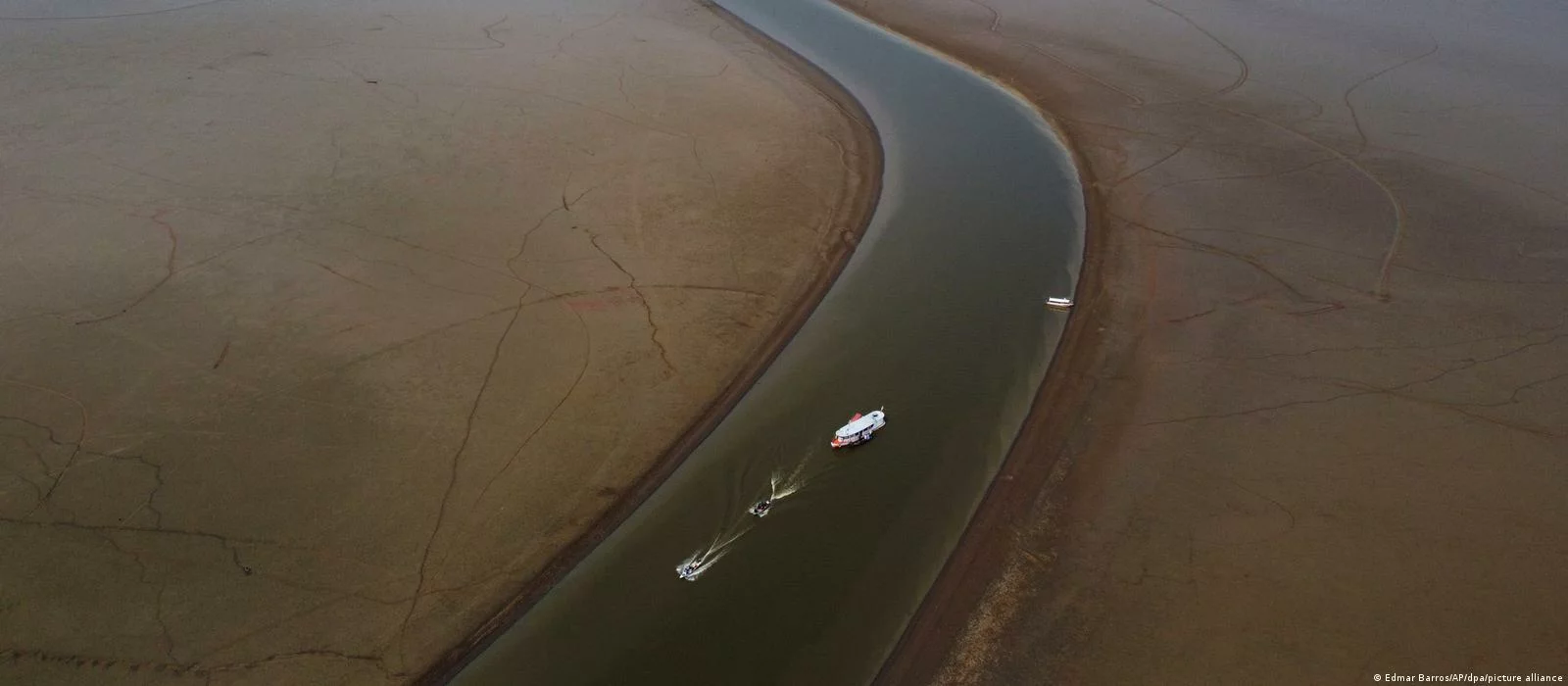
Northern Italy is experiencing its worst drought in 70 years. The Po, Italy's longest river, has been a crucial transportation hub throughout history, helping the north of the country grow into an industrial powerhouse. Experts say the river's water level is now nearly three meters below the zero mark, well below the seasonal average. In early July, the Italian government declared a state of emergency in five regions of the country because of this natural phenomenon.
About one-third of Italy's population (17 million people) lives in the Po River region, as well as more than half of the country's pig and cattle population. The drought has jeopardized the supply of olive oil and rice for risotto, which could lead to a 50% price increase.
France is experiencing its worst drought since record-keeping began in 1958. Water restrictions have been imposed across much of the country, and the corn crop is expected to be nearly 20% lower than in 2021, the Agriculture Ministry said.
Portugal recorded its hottest July on record, with 99% of the country in a state of severe or extreme drought. According to the IPMA meteorological service, the average temperature was just over 40 °C, almost three degrees higher than normal for July.
About 75% of Romania's territory is suffering from drought. The country's grain harvest is projected to drop by 30 million tons.
More than 43% of US states are currently experiencing drought.
Drought has been declared in parts of England, which is expected to lead to water use restrictions. According to the National Drought Management Group, by 2050, some rivers could have 80% less water in the summer, and temperatures could become 7 degrees higher as a result of climate change.
An up-to-date drought monitoring map is available on the website.
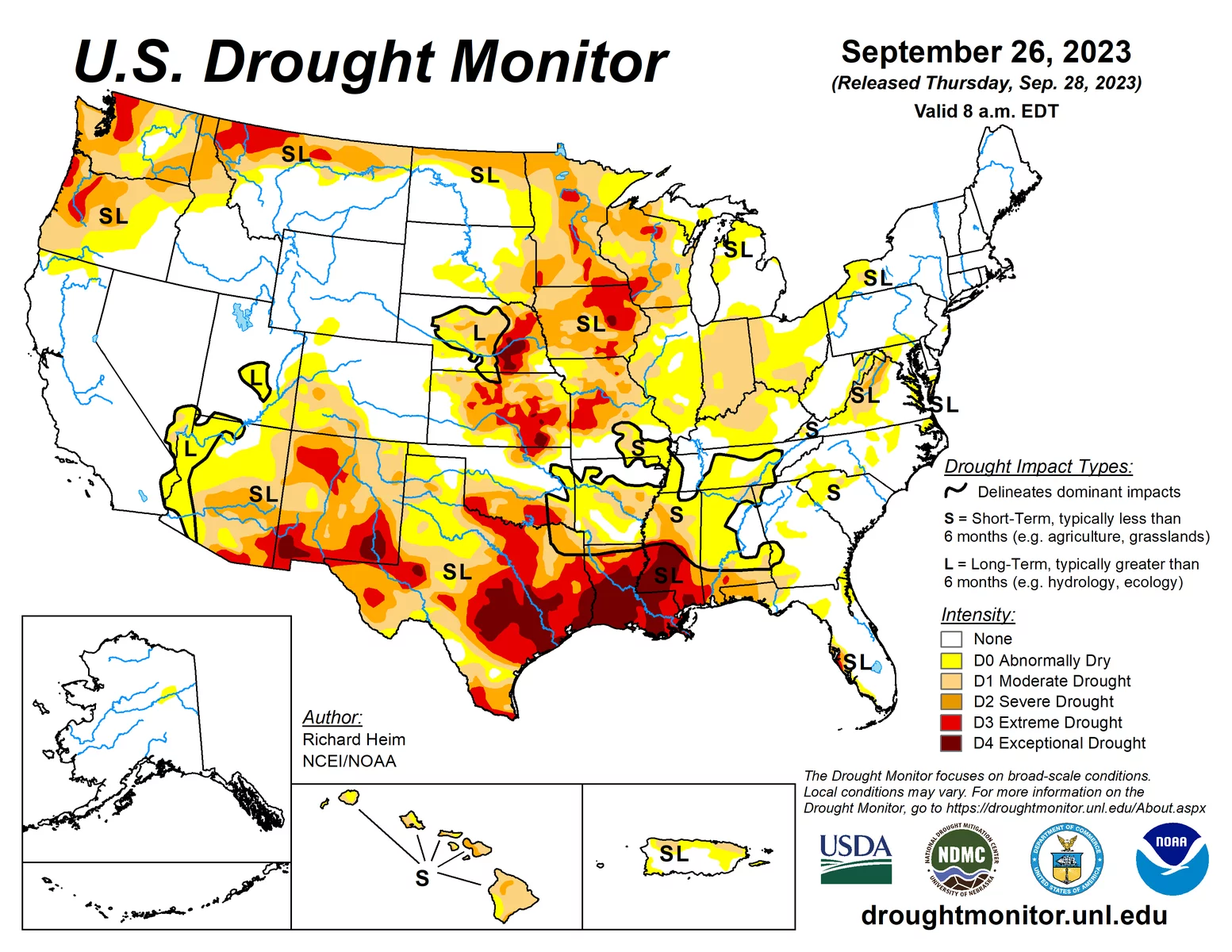
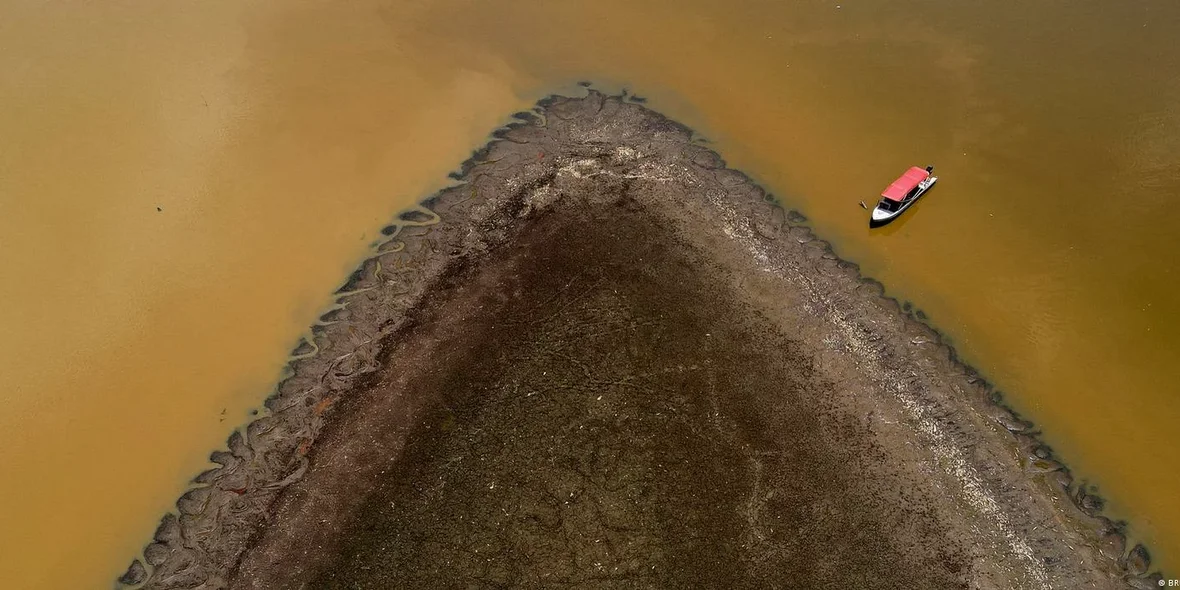
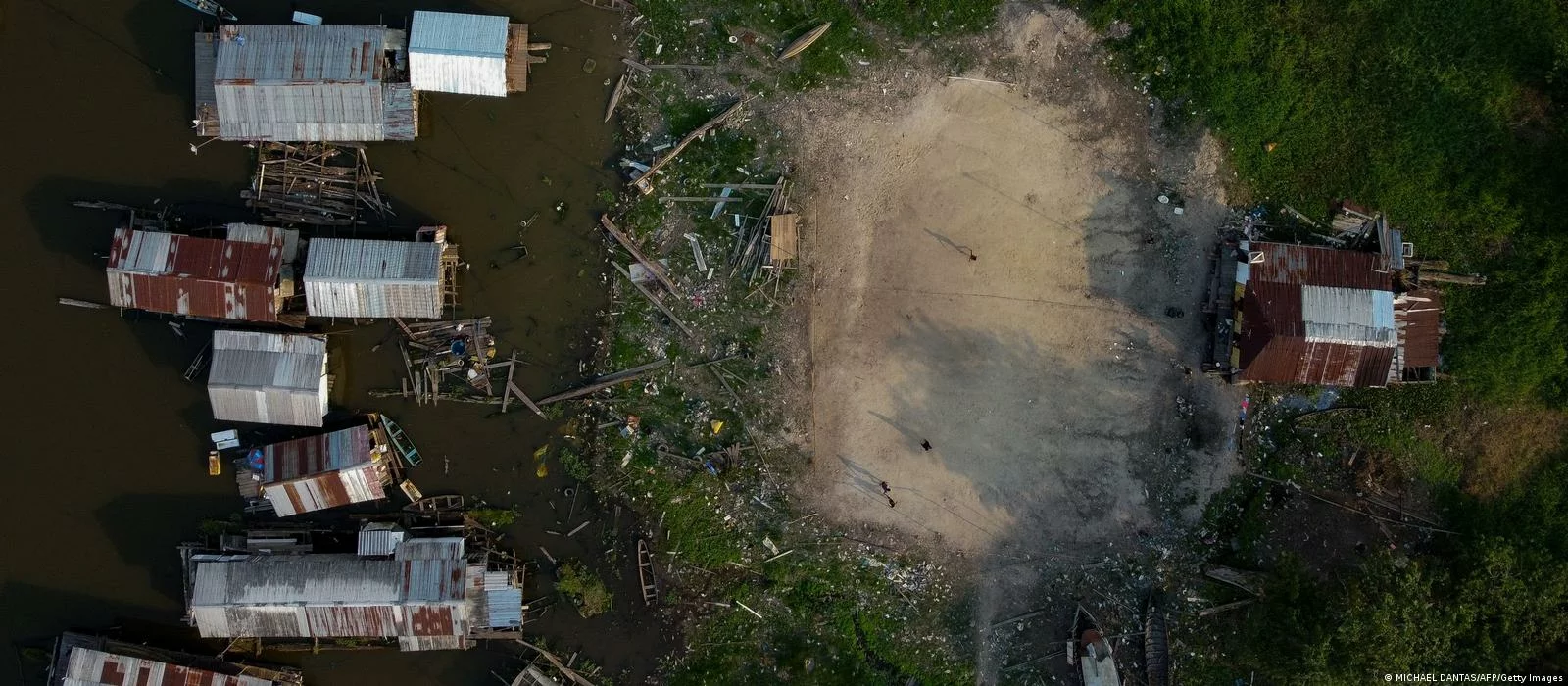
What's happening to the Amazon rainforest right now?
According to a recent CNN report, more than a hundred dolphins have been found dead in the Brazilian Amazon due to a historic drought and record high water temperatures that exceeded 102 degrees Fahrenheit in some places. According to the Mamiraua Institute, all of the dead dolphins were found in Lake Tefe within the last seven days. The institute suggested that about half a million people could be affected by this drought by the end of the year.
The Amazon rainforest has experienced droughts in the past. A recent study found that during the 2015–16 El Niño, the Amazon rainforest experienced record-high temperatures and severe drought. The associated mega-fires resulted in the death of about 2.5 billion trees and plants and the release of 495 million tons of CO2 over an area representing 1.2% of the total area of the Brazilian Amazon rainforest and 1% of the entire biome.
Scientists predict that the record drought in the Amazon basin will last until at least January 2024. This entails, among other things, severe economic consequences for the region, where many residents live off fishing.



Why did 2023 get so hot? A comparison with the ten warmest years on record
According to the European Union's Copernicus Climate Change Service, this summer was the hottest on record “by a wide margin.” The average global temperature this summer was 16.77 degrees Celsius (62.19 degrees Fahrenheit), 0.66 degrees Celsius above the 1990–2020 average.
According to the National Center for Environmental Information (NCEI), the 2023 temperature anomalies are compared to the ten warmest years on record: 2016 (1), 2020 (2), 2019 (3), 2017 (4), 2015 (5), 2022 (5), 2018 (7), 2021 (7), 2014 (9), and 2010 (10). The graph compares the 2023 temperature anomalies (black line) with the ten warmest years on record.
Thus, 2016 was the warmest year on record, and 2023 is not expected to surpass it.
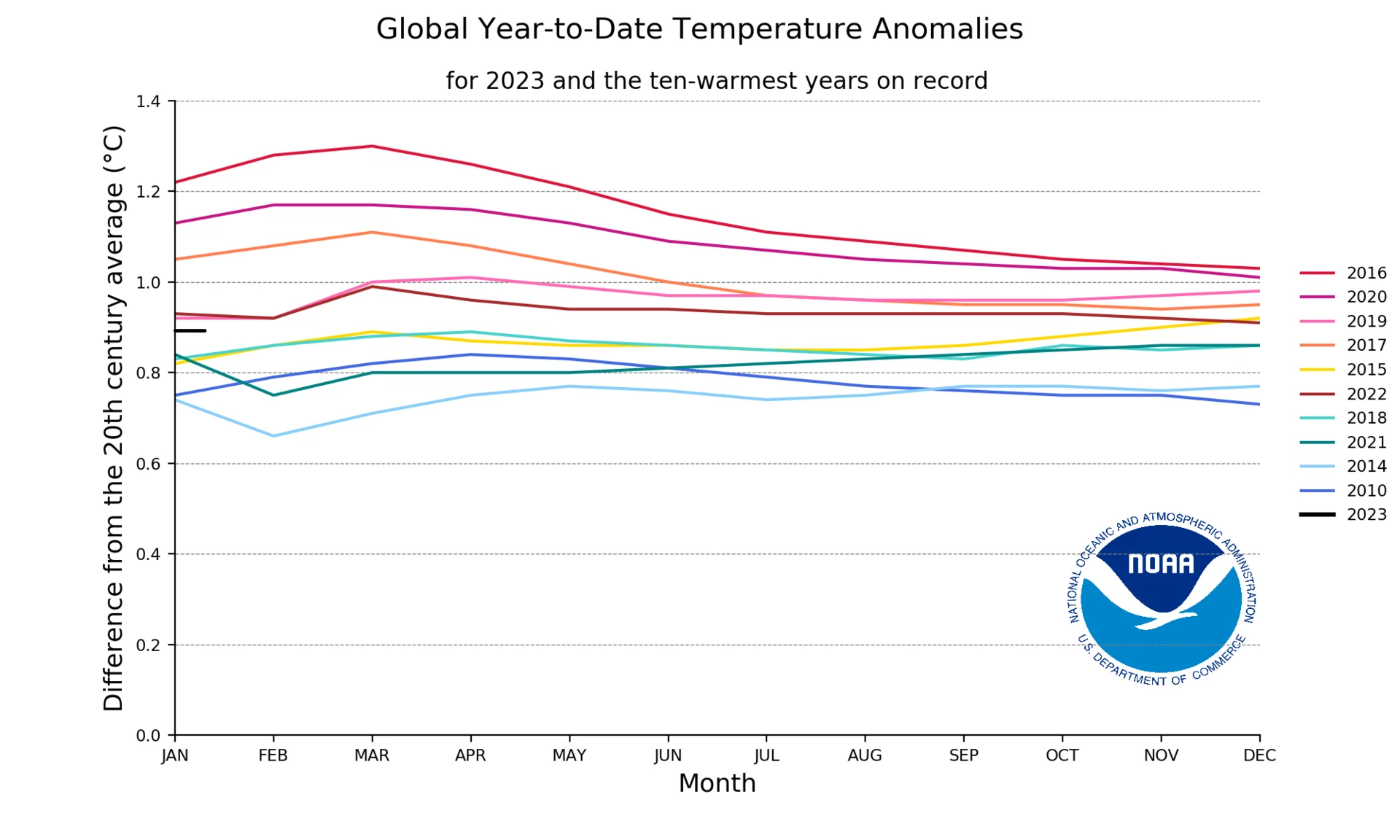
The worst droughts in history
Here are some of the worst droughts in history that have left a deep mark on humanity's memory.
The Dust Bowl drought in the United States (1930s)
One of the most famous and devastating droughts in U.S. history was the so-called Dust Bowl, which raged in the 1930s. This drought covered nearly the entire state, spreading over an area of about 100 million acres. As a result of the drought, millions of acres of fertile soil were destroyed, and many agricultural areas were turned into barren deserts. This resulted in massive population migrations and huge agricultural losses.
Drought in Africa (1981–1984)
The drought that raged in Africa in the early 1980s affected more than 20 African countries, leading to famine and disaster. Hundreds of thousands of people died as a result.
Drought in Australia (2001-2009)
Australia, known for its hot climatic conditions, experienced one of the longest and most severe droughts in its history between 2001 and 2009. This drought affected much of the country, leading to dwindling water supplies, falling reservoir levels, and the destruction of farmland. Many farmers and residents of Australia lost their sources of income and were forced to cope with the lack of water.
Drought in China (1876–1879)
The drought in China is one of the worst in that country's history. Between 1876 and 1879, it led to mass starvation and the deaths of millions of people.
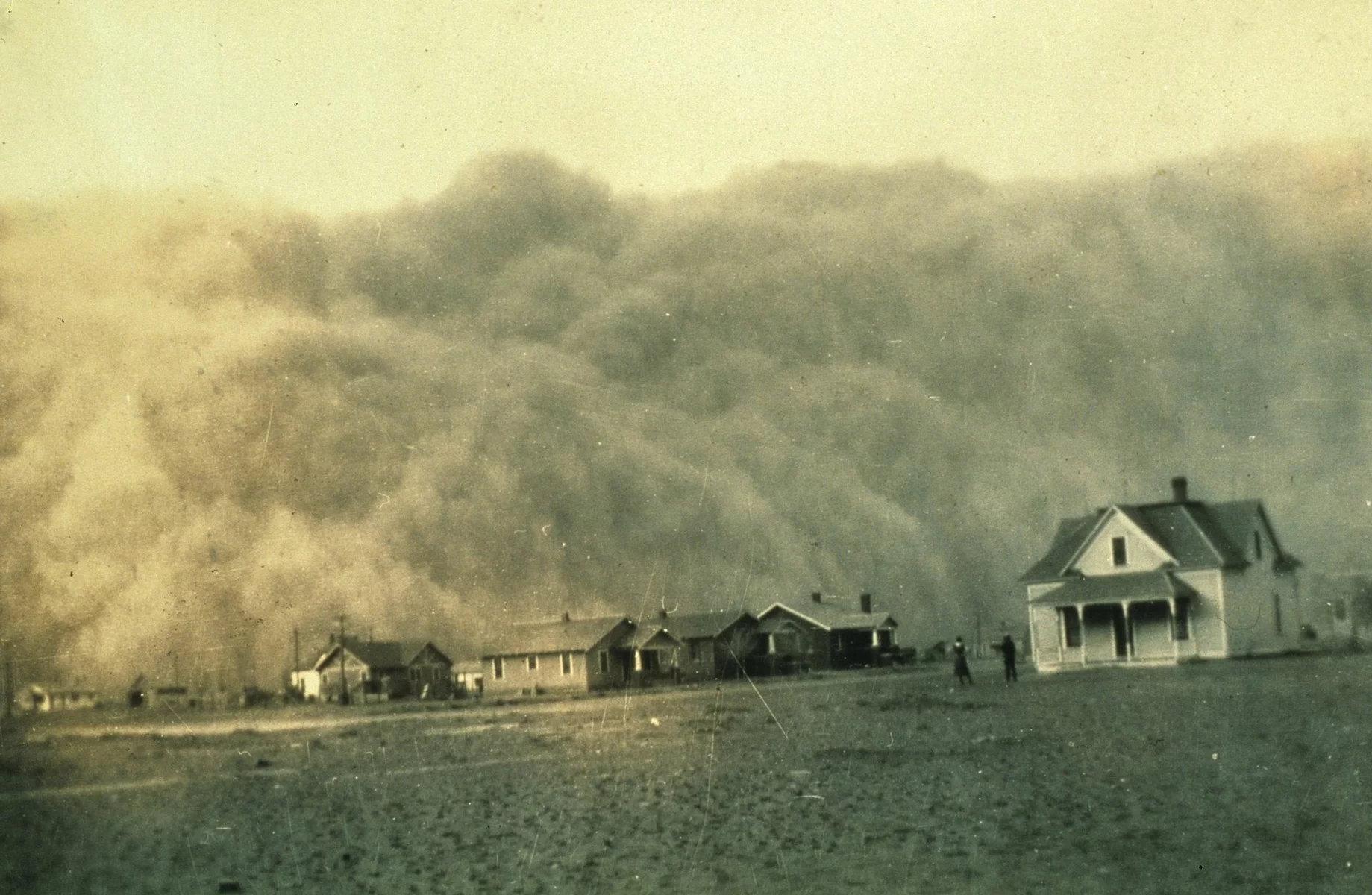

A dust storm in Texas, 1935.
Main photo: Bruno Kelly/Reuters
Author
I am responsible for editorial work. I write expert interviews and guides.



















