
Everything is better than expected. The economic outlook for the EU countries
Steadily rising prices, high inflation and declining GDP growth in most EU countries have a direct impact on the global real estate market. The European Union has prepared an economic outlook for the early 2023-2024, and it seems that the situation is better than expected.
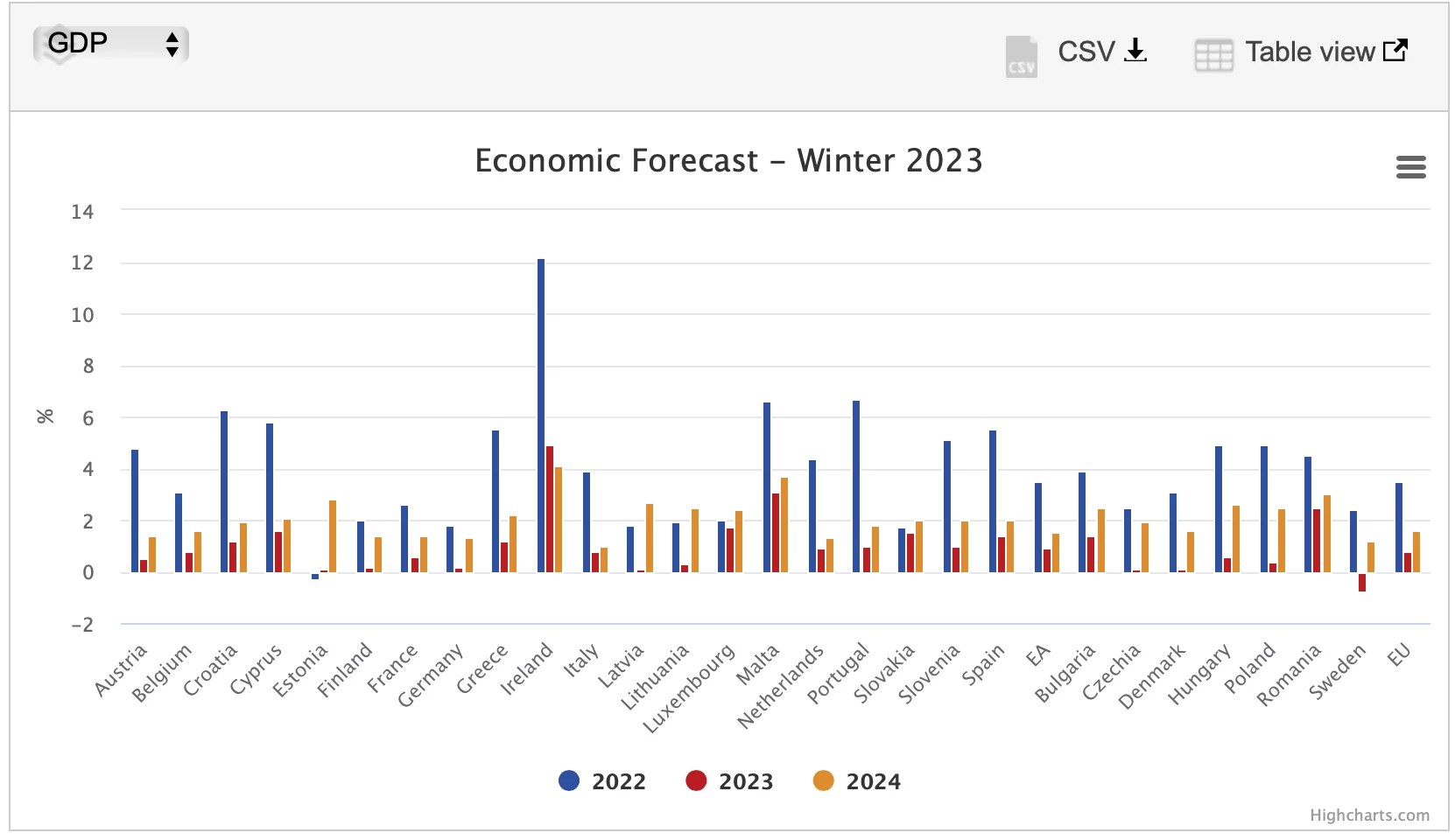
The EU economy entered 2023 on better grounds than had been predicted in the fall. The economy is expected to grow by up to 0.8% in the EU and 0.9% in the Eurozone. Meanwhile, inflation will gradually decline in both 2023 and 2024. Despite exceptional adverse shocks, the EU economy avoided the fourth-quarter contraction predicted in the fall outlook. The annual growth rate in 2022 is currently estimated at 3.5 percent in both the EU and the Eurozone. Growth rates in 2024 are expected to be 1.6% and 1.5% for the EU and the Eurozone, correspondingly.
Continued diversification of supply sources and a sharp drop in consumption have left gas storage levels above the seasonal average in recent years, and the wholesale price of gas has fallen. In addition, the EU labor market continued to perform strongly, with the unemployment rate remaining at a record low of 6.1 percent through the end of 2022.
However, risks still remain. Consumers and enterprises continue to face high energy costs, and core inflation was still rising more in January, further eroding the purchasing power of households. As inflationary pressures persist, monetary tightening will continue, weighing on business activity and putting a drag on investment.
Inflation is expected to ease after peaking in 2022. After reaching an all-time record high of 10.6% in October, inflation has declined and in January fell to 8.5% in the Eurozone. Inflation is projected to fall from 9.2% in 2022 to 6.4% in 2023 and to 2.8% in 2024 in the EU. In the Eurozone, it is predicted to slow from 8.4% in 2022 to 5.6% in 2023 and to 2.5% in 2024.
While uncertainty around the outlook remains high, the risks for growth are generally balanced. Domestic demand could be higher than expected if the recent decline in wholesale gas prices passes through with stronger consumer prices and consumption proves more resilient. Nevertheless, a potential reversal of this decline cannot be ruled out in the context of ongoing geopolitical tensions.
Risks of inflation remain largely tied to the development of energy markets, reflecting some of the identified risks for growth. Especially in 2024, the risks of higher inflation prevail, as price pressures could be greater than expected if wage growth settles at above-average rates over a sustained period.
Source: EU official website


















